Navigating the complexities of network management demands robust tools, and Clash for Windows stands out as a premier solution.
Understanding Rule Providers is essential for optimizing this powerful application. This article delves into what Rule Providers are, their various types, and how to effectively set them up and manage them within Clash for Windows. Prepare to unlock the full potential of your network configuration as we explore strategies to enhance your experience.
Utilizing appropriate rule providers in Clash for Windows can significantly enhance security and optimize network performance for users.
Notable rule providers include:
- Surge
- Quantumult X
- Clash itself
Surge offers advanced rule management capabilities, allowing users to set intricate conditions based on IP and domain types, thereby ensuring precise control over traffic flow. Quantumult X is recognized for its user-friendly interface, which presents dynamic filtering options suitable for users with limited technical expertise.
Additionally, Clash’s built-in rule provider facilitates seamless integration with customizable YAML configurations. By selecting the appropriate provider based on individual technical capabilities and specific requirements, users can achieve an optimized balance between security and performance.
What Are Rule Providers?
Rule providers consist of predefined configurations that determine how Clash for Windows manages various types of network traffic. These configurations can be customized to meet specific requirements, such as optimizing gaming performance or enhancing streaming quality.
For example, one may utilize a rule provider that prioritizes gaming traffic by directing it through a dedicated server, thereby ensuring low latency. Alternatively, a rule provider could be employed to manage bandwidth for streaming, allowing users to specify which applications receive priority during peak usage periods.
By tailoring these rules according to individual activities, users can substantially enhance their overall network experience and sustain a stable connection.
Types of Rule Providers
There are several categories of rule providers, including those focused on application rules, network protocols, and user-defined policies, each serving distinct and important functions.
Application rules are specifically designed to regulate the behavior of certain applications, such as imposing bandwidth restrictions on streaming platforms during peak usage hours.
Network protocol rules control the flow of traffic based on specific protocols; for instance, prioritizing Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) traffic over general web browsing significantly enhances call quality.
User-defined policies enable customization, allowing users to establish rules that cater to their specific needs, such as blocking access to social media during work hours.
Each category plays a critical role in optimizing performance and enhancing security within a network.
Setting Up Clash for Windows
The proper setup of Clash for Windows requires a systematic approach to installation and configuration, which is essential for ensuring optimal performance and security.
Installation Steps
To install Clash for Windows, begin by downloading the latest version from GitHub, and follow a straightforward installation process that typically takes approximately 15 minutes.
First, ensure that your system meets the following requirements:
- Windows 10 or a newer version
- .NET Framework 4.7.2
- A minimum of 1 GB of RAM
Next, navigate to the Clash for Windows GitHub page, locate the most recent release under the ‘Releases’ section, and download the installer.
After the download is complete, run the installer and adhere to the prompts to finalize the setup. It is advisable to temporarily disable your antivirus software, as it may inadvertently block installation files.
Upon successful installation, configure your settings and import your YAML profile to facilitate effective proxy management.
Initial Configuration
Once installed, the initial configuration entails setting up proxy settings and defining rule providers, a process that can typically be completed in under 30 minutes.
To begin, launch Clash for Windows and navigate to the ‘Profiles’ section. Here, enter your desired proxy server addresses, ensuring that protocols such as Vmess or Shadowsocks are selected appropriately.
Subsequently, proceed to the ‘Rules’ tab, where you can define your rule providers. Consider utilizing predefined rules from Clash’s GitHub repository to facilitate efficient traffic management.
To enhance performance, it is advisable to adjust the DNS settings to use a faster DNS server, such as Cloudflare (1.1.1.1). Additionally, it is important to regularly monitor the connection status to ensure optimal operation.
Using Rule Providers Effectively
Utilizing rule providers in Clash for Windows effectively can significantly improve network performance and enhance security measures.
How to Add Rule Providers
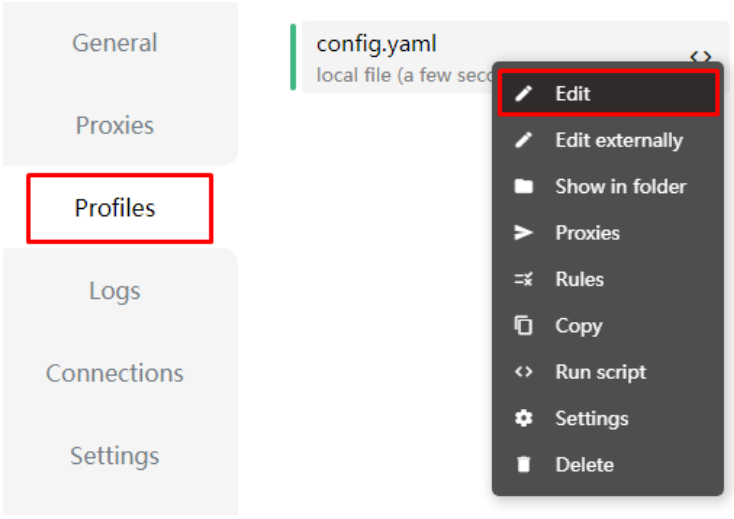
Adding rule providers in Clash for Windows requires navigating the user interface and inputting specific YAML configuration files.
To begin, open the Clash for Windows application and proceed to the ‘Profiles’ tab. Click on ‘Edit’ adjacent to the profile you wish to modify.
You will need to add your rule providers in the YAML format, which typically appears as follows:
```yaml rule-providers: provider_name: type: http behavior: classical path:./provider.yaml ```
It is essential to source reliable providers from GitHub repositories or community forums, as these sources often contain up-to-date configurations. Additionally, it is important to meticulously check the syntax; any errors could result in the malfunction of your rules.
Managing Rule Providers
Effectively managing rule providers necessitates the implementation of regular updates, continuous monitoring of performance metrics, and timely adjustments to settings as required.
To begin, it is advisable to establish a routine for reviewing performance metrics on a weekly basis. Utilizing analytics tools such as Google Analytics or SEMrush can facilitate the tracking of engagement and traffic performance for each content source.
Should a specific provider exhibit a decline in performance persisting beyond a two-week period, it would be prudent to consider its replacement. Settings should be maintained based on insights derived from analytics; for instance, it may be beneficial to increase the frequency of checks for high-performing feeds while decreasing it for those that demonstrate underperformance.
Additionally, regularly refreshing content sources on a quarterly basis can contribute to maintaining relevance and optimizing audience engagement.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Users may experience common issues with rule providers in Clash for Windows, which can be addressed through systematic troubleshooting procedures.
Common Errors with Rule Providers
Common errors associated with rule providers include misconfigured settings, outdated YAML files, and compatibility issues with network protocols.
Misconfigured settings can result in improper data flow; therefore, it is imperative to ensure that all parameters align with the intended configuration. Outdated YAML files frequently contain deprecated syntax, making it essential to regularly update these files in accordance with the latest documentation.
Compatibility issues may occur when different network protocols are utilized, such as the mixing of HTTP with HTTPS. It is advisable to verify that settings are uniform across all components.
Utilizing testing tools such as Postman or cURL can facilitate the prompt identification and resolution of these errors, thereby ensuring seamless integration and functionality.
Resolving Configuration Problems
Resolving configuration problems typically requires a systematic approach to revising YAML syntax and verifying compliance with current rules. It is advisable to begin by utilizing a YAML validator, such as ‘YAML Lint’ or ‘Online YAML Parser,’ to identify any syntax errors. Common issues may include misplaced colons or inconsistent indentation.
For instance, one should ensure that list items are correctly formatted with hyphens.
Following the correction of syntax errors, it is important to review the configuration for any deprecated rules by consulting the most recent documentation associated with the specific application being configured. This step is critical, as outdated rules can result in unexpected behaviors. Testing changes incrementally allows for the efficient isolation of issues.
